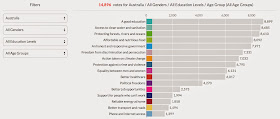
One of the starkest differences between Australia and the US's Government 2.0 movements is the mandate and level of support provided officially by our most influential elected officials.
In the US Government 2.0 has been championed both by the President and by leading politicians on both sides of their political divide.
Regardless of ideology there has been a recognition by US political institutions that involving citizens more deeply in governance is a necessity in an age when almost every individual voter has access to the world's knowledge, the ability to organise, publish and influence public views in ways unprecedented in history.
An example of this is taking place today. A civic hackathon at the White House organised by the government to marshall the collective brainpower of the country's smartest people to improve one of the US government's most visible Government 2.0 tools.
The #WHhackathon has been organised to build on the US's We The People epetition site, which allows all US citizens to create and contribute to online petitions that, if they reach 100,000 petitioners, receives an official response from the US government.
The US government released the code to We The People in 2012 as open source, allowing governments around the world to reuse it to create their own epetition sites.
More recently the US government created an API for We The People, allowing other petition sites, organisations and individuals to read data from the platform and present it in new ways, creating new services.
The hackathon in the White House is designed to build on this API, creating value for the government and community while increasing government transparency and empowering citizens to influence the representatives elected to govern them.
Could this happen in Australia?
Could an Australian Prime Minister make a public statement, and unbreakable commitment, to openness in government, to investing in initiatives that help citizens participate in the governance of the country and opening up the black box of decision-making to give citizens real ways to influence outcomes?
Could an Australian Prime Minister take a leadership role in recognising that governments can't and no longer have to do all the heavy lifting in designing the systems for government, developing policy and services or achieving positive outcomes for citizens?
Could they invite in voices beyond the usual lobbyist suspects to contribute actively to the success of the country, to help in cutting costs, innovating and transforming our government to meet the challenges of the 21st century?
Well yes - an Australian Prime Minister could.
However we are yet to see one with this vision, and as a result Australia is being left behind.
Australia doesn't lack the ability, we don't lack the expertise in the public sector and we don't lack the technical smarts.
All we lack is political vision and commitment.
The US government released the code to We The People in 2012 as open source, allowing governments around the world to reuse it to create their own epetition sites.
More recently the US government created an API for We The People, allowing other petition sites, organisations and individuals to read data from the platform and present it in new ways, creating new services.
The hackathon in the White House is designed to build on this API, creating value for the government and community while increasing government transparency and empowering citizens to influence the representatives elected to govern them.
Could this happen in Australia?
Could an Australian Prime Minister make a public statement, and unbreakable commitment, to openness in government, to investing in initiatives that help citizens participate in the governance of the country and opening up the black box of decision-making to give citizens real ways to influence outcomes?
Could an Australian Prime Minister take a leadership role in recognising that governments can't and no longer have to do all the heavy lifting in designing the systems for government, developing policy and services or achieving positive outcomes for citizens?
Could they invite in voices beyond the usual lobbyist suspects to contribute actively to the success of the country, to help in cutting costs, innovating and transforming our government to meet the challenges of the 21st century?
Well yes - an Australian Prime Minister could.
However we are yet to see one with this vision, and as a result Australia is being left behind.
Australia doesn't lack the ability, we don't lack the expertise in the public sector and we don't lack the technical smarts.
All we lack is political vision and commitment.