Monday, May 06, 2019
Mapping Canberra's startup ecosystem | Tweet |
I've had a continuing interest in start-up ecosystems across Australia, having been a member of several of these ecosystems & helping to mentor and support a range of start-ups over the years.
I've maintained a Canberra ecosystem map for about four years now, mostly for my own interest and to understand some of the relationships between different players and the startups they support.
This was inspired by work by BlueChilli on the defunct StartRail maps, which was based on some of the international work portraying startup ecosystems in the style of metro rail maps. Unfortunately they focused on Sydney and Melbourne, missing some of the smaller, yet equally vibrant, scenes in Perth, Brisbane and Canberra, all of which I am linked to in various ways.
Recently I've seen some sterling work by Gordon Whitehead mapping the startup ecosystem for the Hunter & Central Coast, which had been reinterpreted by Brian Hill of Laughing Mind.
As such I've decided to share my Canberra startup ecosystem map for anyone interested.
Also keep an eye out for the work by Chad Renando at StartStatus, who is engaged in a national effort as part of his Phd, which should provide a broader view of the Australian startup ecosystem as a whole (which tends to be city-based with a few cross-ties of various strength).
Chad has also done some intensive work looking at models for measuring startup ecosystems and identifying their strengths & weaknesses that will be very valuable to government, not-for-profit and corporate interests in years to come.
As for Canberra - here's my humble contribution....
Monday, November 12, 2018
The #GovHack 2018 National Awards by the numbers | Tweet |
I shared this via a Twitter thread, but wanted to include it here for longevity.
To learn more about GovHack and the National Red Carpet event, which I attended as a representative of my team & the ACT Spirit of GovHack winner (and finalist for the National Spirit of GovHack), visit www.govhack.org




I've analysed the #opendata & here's the #GovHack 2018 Awards by the numbers:
There were 33 National Awards (including Spirit & Government Participation).
A total 88 Awards were issued: 33 First places, 18 Runner-ups and 37 Hon. Mentions.
Excluding Spirit of #GovHack & Gov Participation 59 teams won at least one Award.
Two teams won 3 Awards each:
Another 16 teams won two #GovHack Awards.
41 #GovHack teams won 1 award: 13 won a First, 5 a Runners-up & 23 a Hon. Mention.
By state/territory, inc. State/Local Government Participation & Spirit of #GovHack, National #GovHack Awards followed population size (except ACT which punched above its weight):
The #GovHack results looks a little different in detail, with Victoria winning more First places than anyone else & Queensland tying with NSW! (the NA are the National Government Participation Awards which I excluded as they give ACT an unfair bonus)
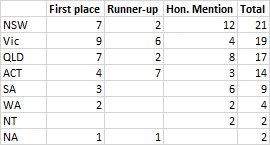
In fact, using a 3-2-1 scoring system for First Place, Runner-up and Hon. Mention, Victoria outscores NSW, and ACT even closer to the top three in the raw #GovHack award numbers.
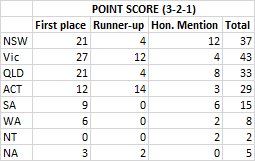
Finally, looking at #GovHack National Awards by venue, the central city venues did better than regional locations in all cases, except in Queensland - where the Sunshine Coast won more awards than anywhere else in Qld, including Brisbane... Amazing work guys!!!
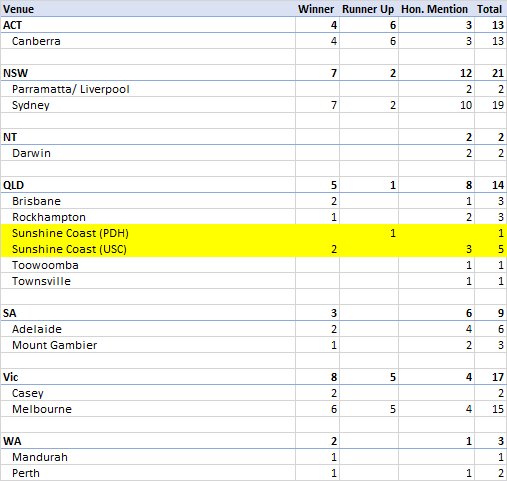
And here's the table of National #GovHack Awards by venue...
And that's the wrap on the by the numbers Awards for #GovHack 2018.
My data is still a bit messy, but I'll clean it up and put it in a Google sheet at some point in the next week so others can access it.
To learn more about GovHack and the National Red Carpet event, which I attended as a representative of my team & the ACT Spirit of GovHack winner (and finalist for the National Spirit of GovHack), visit www.govhack.org




I've analysed the #opendata & here's the #GovHack 2018 Awards by the numbers:
There were 33 National Awards (including Spirit & Government Participation).
A total 88 Awards were issued: 33 First places, 18 Runner-ups and 37 Hon. Mentions.
Excluding Spirit of #GovHack & Gov Participation 59 teams won at least one Award.
Two teams won 3 Awards each:
- Tiny Happy People Hacking: 1 First place, 1 Runner-up, 1 Hon. Mention
- in time: 2 Runner-ups & 1 Hon. Mention
Another 16 teams won two #GovHack Awards.
- 5 teams won 2 First places! (as.numeric, Blockheads, Tartans-AU, insolvit & TeamTeam)
- Another 5 won 1 First place, with 3 also winning a Runner-up (Big Orange Brain, Oakton, TechPreppers) and 2 also an Hon. Mention (DataCake & TeamX).
41 #GovHack teams won 1 award: 13 won a First, 5 a Runners-up & 23 a Hon. Mention.
- Firsts:
ARVIS, Bachmanns and Fulwoods, Get Active USC, Hack aPEEL, I’m Learnding, Living Spirit, Lucky Shot, Motley Crue, Team Marika, Team Rocket, Technotelecomnicon, The Ogrelords, This Place
By state/territory, inc. State/Local Government Participation & Spirit of #GovHack, National #GovHack Awards followed population size (except ACT which punched above its weight):
- NSW won 21
- Vic won 19
- Qld won 17
- ACT won 14
- SA won 9
- WA won 4
- NT won 2
- Tas won 0 (sorry folks)
The #GovHack results looks a little different in detail, with Victoria winning more First places than anyone else & Queensland tying with NSW! (the NA are the National Government Participation Awards which I excluded as they give ACT an unfair bonus)

In fact, using a 3-2-1 scoring system for First Place, Runner-up and Hon. Mention, Victoria outscores NSW, and ACT even closer to the top three in the raw #GovHack award numbers.

Finally, looking at #GovHack National Awards by venue, the central city venues did better than regional locations in all cases, except in Queensland - where the Sunshine Coast won more awards than anywhere else in Qld, including Brisbane... Amazing work guys!!!
And here's the table of National #GovHack Awards by venue...

And that's the wrap on the by the numbers Awards for #GovHack 2018.
My data is still a bit messy, but I'll clean it up and put it in a Google sheet at some point in the next week so others can access it.
Tags:
data,
govhack,
innovation,
open data,
open policy
Thursday, May 17, 2018
Guest Post: FatigueHack - Hackathon done right | Tweet |
This is a guest post from Jayden Castillo, a colleague of mine at Accenture and an active member of Canberra's innovation community. Read the original post at LinkedIn:
I recently attended the Australian Trucking Association (ATA)'s Hackathon aiming to target driver fatigue, aptly named 'FatigueHack'. I'm fairly new to Hackathons, this was my second after the AUSTRAC Codeathon in March (where I was a mentor), and my first experience as a participant along side two of my Accenture team mates.
For those unfamiliar with the concept, a Hackathon is a rapid solution environment where competitors are required to address complex challenges in a short amount of time, and come up with a working prototype to illustrate their concept. In this case, teams had 2 days to develop a viable business model which is capable of addressing fatigue in the trucking industry. Following these two days, each of the 8 participating teams had to pitch their solutions to judges and the top 3 pitched to the entire Australian Trucking Association Annual Conference delegation.
I find hackathons to be a fantastic opportunity to show what's possible, and even more impressive, what's possible in just two days. There were a few aspects of FatigueHack in particular which I believe made it exceptional, and demonstrates not only what is possible, but what innovation and solutioning will be like in The New. The 3 points below are the perfect recipe for innovation, which we must all embrace to stay at the cutting edge.
Short Timelines
We all have a tendency to procrastinate, to plan things excessively, and to over analyse. This is a product of the anti-failure mindset we've been groomed for, we naturally try to think out the whole solution and resolve any issues before we actually start doing. Being under quite a strict time limit means there simply isn't enough time for this. You are forced to make decisions and move things along quickly. This means you might not have all the problems solved straight away, but it also means there's less time between idea and the all important testing of your idea, so you can identify and resolve issues much faster.
Probably the most interesting part here was to demonstrate how unnecessary it is to give long timelines to (particularly innovative) projects. When your timeline is short, you cut out what's not important and make big strides in your solution.
Concentrated ideation
They say that innovation happens when ideas collide, and FatigueHack certainly had a lot of colliding ideas. Think and Grow Rich author Napoleon Hill describes this like brainwaves being radiated out into the ether, and being picked up on by other brains on the same wavelength. While this description might a bit unscientific, I believe there is a lot to be said for the buzz created when a lot of excited people are in close proximity. Your confidence goes up, your creativity goes up, and you are generally more open to thoughts and ideas.
Having run remote meetings and workshop sessions in the past, I can definitely attest to the value of having everyone in the same room, even if they're not all working on the same idea. Body language, excitement, drawing, gestures are all things which (still) don't translate well over digital media.
Easy access to expertise
Innovating or designing in a bubble is a dangerous thing to do. It is basically impossible to know if you're on the right track without some kind of feedback, so it becomes really easy to go down the wrong path and either solve the wrong problem or create a solution which nobody wants. I think FatigueHack managed this really well - they ran the Hackathon in the same venue at the same time as the ATA's annual conference. This was invaluable, because it meant if we had any questions at all, we could find an expert on the area within 5 minutes by simply asking around.
Having such easy access to expertise makes innovating much easier. It allows you to validate ideas very quickly, and when we were listening to the truckers talking about their experience it stimulated new ideas quickly. Our ability to iterate and refine was exponentially higher than in a normal workplace, and ideas were changing and evolving in time frames of minutes. I would love to see this translate to my (and everyone's) daily work, because the potential for generating great solutions is enormous.
Closing thoughts
This Hackathon really demonstrated to me what the future of work looks like. By getting a team together in a highly concentrated, intense environment, and providing more information and experts than we could possibly digest in 2 days, there were some fantastic outcomes (the winning idea is moving forward with creating a business!).
My personal mission is to help businesses and organisations think and act like startups, and FatigueHack is a great example of how to do that.
I recently attended the Australian Trucking Association (ATA)'s Hackathon aiming to target driver fatigue, aptly named 'FatigueHack'. I'm fairly new to Hackathons, this was my second after the AUSTRAC Codeathon in March (where I was a mentor), and my first experience as a participant along side two of my Accenture team mates.
For those unfamiliar with the concept, a Hackathon is a rapid solution environment where competitors are required to address complex challenges in a short amount of time, and come up with a working prototype to illustrate their concept. In this case, teams had 2 days to develop a viable business model which is capable of addressing fatigue in the trucking industry. Following these two days, each of the 8 participating teams had to pitch their solutions to judges and the top 3 pitched to the entire Australian Trucking Association Annual Conference delegation.
I find hackathons to be a fantastic opportunity to show what's possible, and even more impressive, what's possible in just two days. There were a few aspects of FatigueHack in particular which I believe made it exceptional, and demonstrates not only what is possible, but what innovation and solutioning will be like in The New. The 3 points below are the perfect recipe for innovation, which we must all embrace to stay at the cutting edge.
Short Timelines
We all have a tendency to procrastinate, to plan things excessively, and to over analyse. This is a product of the anti-failure mindset we've been groomed for, we naturally try to think out the whole solution and resolve any issues before we actually start doing. Being under quite a strict time limit means there simply isn't enough time for this. You are forced to make decisions and move things along quickly. This means you might not have all the problems solved straight away, but it also means there's less time between idea and the all important testing of your idea, so you can identify and resolve issues much faster.
Probably the most interesting part here was to demonstrate how unnecessary it is to give long timelines to (particularly innovative) projects. When your timeline is short, you cut out what's not important and make big strides in your solution.
Concentrated ideation
They say that innovation happens when ideas collide, and FatigueHack certainly had a lot of colliding ideas. Think and Grow Rich author Napoleon Hill describes this like brainwaves being radiated out into the ether, and being picked up on by other brains on the same wavelength. While this description might a bit unscientific, I believe there is a lot to be said for the buzz created when a lot of excited people are in close proximity. Your confidence goes up, your creativity goes up, and you are generally more open to thoughts and ideas.
Having run remote meetings and workshop sessions in the past, I can definitely attest to the value of having everyone in the same room, even if they're not all working on the same idea. Body language, excitement, drawing, gestures are all things which (still) don't translate well over digital media.
Easy access to expertise
Innovating or designing in a bubble is a dangerous thing to do. It is basically impossible to know if you're on the right track without some kind of feedback, so it becomes really easy to go down the wrong path and either solve the wrong problem or create a solution which nobody wants. I think FatigueHack managed this really well - they ran the Hackathon in the same venue at the same time as the ATA's annual conference. This was invaluable, because it meant if we had any questions at all, we could find an expert on the area within 5 minutes by simply asking around.
Having such easy access to expertise makes innovating much easier. It allows you to validate ideas very quickly, and when we were listening to the truckers talking about their experience it stimulated new ideas quickly. Our ability to iterate and refine was exponentially higher than in a normal workplace, and ideas were changing and evolving in time frames of minutes. I would love to see this translate to my (and everyone's) daily work, because the potential for generating great solutions is enormous.
Closing thoughts
This Hackathon really demonstrated to me what the future of work looks like. By getting a team together in a highly concentrated, intense environment, and providing more information and experts than we could possibly digest in 2 days, there were some fantastic outcomes (the winning idea is moving forward with creating a business!).
My personal mission is to help businesses and organisations think and act like startups, and FatigueHack is a great example of how to do that.
Tags:
challenge,
community,
contest,
engagement,
hackathon,
ideas market
Tuesday, May 15, 2018
If exposure to social media messages can affect human moods & more, what responsibility do digital marketers & organisations hold? | Tweet |
There's a lot of evidence available now that the emotional tone of the messaging that people are exposed to on social media goes on to affect their mood, posting behaviour, and aspects of their health and actions.
A study by Facebook and Cornell University in 2012 (published in 2014) that involved modifying the emotional valance of posts on 689,003 users' Facebook News Feeds, putting aside the ethics of experimenting unknowingly on their users, evidenced a strong link between what people saw in their Feed and the emotional valance of what they posted afterwards.
The study postulated that 'emotional contagion' was very strong in social media channels, with the capability for peoples' moods and behaviours to be significantly altered through exposure to messaging that expressed certain tones or viewpoints.
Other research has validated connections between the emotional tone of the social and digital media we consume and the behaviours we exhibit - which really should not come as a surprise as it is the basis of the advertising, propaganda and marketing industries (using emotional triggers to stimulate behaviour change) and is readily visible in the mood swings evident in forum, Facebook and Twitter conversations over time.
So if we can be fairly confident that emotional tone is 'contagious', and that emotions then influence behaviours, what is the responsibility of communicators and marketers when using digital and social media to engage audiences at scale to 'set' the right tone?
I've long been a proponent of having clear community guidelines for communities that government agencies and companies establish in order to set the appropriate context and tone for conversations up front. Failing to do this can lead to communities rapidly moving beyond the influence of the establishing organisation and having conversational tone going to places that are undesirable or damaging.
However even when posting or promoting material through general digital channels there can be a significant impact on audience mood and behaviour depending on the approach taken by the organisation - even for 'emotionless' statements of fact that could be perceived in negative or positive ways.
Simply stating the facts and taking no responsibility for the audience's emotional reaction is a common, but flawed strategy, when it is used as a way to justify that the organisation is blameless as to how others react (and I have to admit that I've used this to 'excuse' myself in personal conversations as well).
While it isn't always possible to predict how a group, or particularly how an individual, will react to a given message, we can design and test our messaging to bias toward a particular emotional and behavioural response.
This could be seen as manipulative, but arguably is no more manipulative than dropping unpleasant information in a factual manner and then blaming the negative reaction on the 'receivers'. Whenever we communicate we are aim to have an impact, so it only behooves us to strive to minimise any harm that could come from our communications as far as is possible.
So when participating or advertising online, digital marketers need to develop a sound understanding of their audiences and be mindful of the impacts of our communications - much as how newspapers now provide support line contact details at the end of disturbing articles.
When emotional contagion takes hold and amplifies an emotional or behavioural response - whether for good or ill, the impacts can be enormous - and digital marketers and communicators need to own their contribution in these cases.
A study by Facebook and Cornell University in 2012 (published in 2014) that involved modifying the emotional valance of posts on 689,003 users' Facebook News Feeds, putting aside the ethics of experimenting unknowingly on their users, evidenced a strong link between what people saw in their Feed and the emotional valance of what they posted afterwards.
The study postulated that 'emotional contagion' was very strong in social media channels, with the capability for peoples' moods and behaviours to be significantly altered through exposure to messaging that expressed certain tones or viewpoints.
Other research has validated connections between the emotional tone of the social and digital media we consume and the behaviours we exhibit - which really should not come as a surprise as it is the basis of the advertising, propaganda and marketing industries (using emotional triggers to stimulate behaviour change) and is readily visible in the mood swings evident in forum, Facebook and Twitter conversations over time.
So if we can be fairly confident that emotional tone is 'contagious', and that emotions then influence behaviours, what is the responsibility of communicators and marketers when using digital and social media to engage audiences at scale to 'set' the right tone?
I've long been a proponent of having clear community guidelines for communities that government agencies and companies establish in order to set the appropriate context and tone for conversations up front. Failing to do this can lead to communities rapidly moving beyond the influence of the establishing organisation and having conversational tone going to places that are undesirable or damaging.
However even when posting or promoting material through general digital channels there can be a significant impact on audience mood and behaviour depending on the approach taken by the organisation - even for 'emotionless' statements of fact that could be perceived in negative or positive ways.
Simply stating the facts and taking no responsibility for the audience's emotional reaction is a common, but flawed strategy, when it is used as a way to justify that the organisation is blameless as to how others react (and I have to admit that I've used this to 'excuse' myself in personal conversations as well).
While it isn't always possible to predict how a group, or particularly how an individual, will react to a given message, we can design and test our messaging to bias toward a particular emotional and behavioural response.
This could be seen as manipulative, but arguably is no more manipulative than dropping unpleasant information in a factual manner and then blaming the negative reaction on the 'receivers'. Whenever we communicate we are aim to have an impact, so it only behooves us to strive to minimise any harm that could come from our communications as far as is possible.
So when participating or advertising online, digital marketers need to develop a sound understanding of their audiences and be mindful of the impacts of our communications - much as how newspapers now provide support line contact details at the end of disturbing articles.
When emotional contagion takes hold and amplifies an emotional or behavioural response - whether for good or ill, the impacts can be enormous - and digital marketers and communicators need to own their contribution in these cases.
Tags:
communication,
community,
digital,
marketing,
social media
Wednesday, April 25, 2018
Governments are getting serious about innovation capability | Tweet |
The Australian government has been touting the importance of innovation for several years now, with the Coalition's innovation agenda recently conceded to be a political failure due to its lack of resonance with the Australian public.
However underneath the politics, government agencies across Australia and New Zealand have been vigorously expanding their innovation capability, as the The Policy Lab at Melbourne University recently reported.
Notably a number of these units remain new, with a quarter less than 12 months old, and more than half less than two years old, and small, with half employing 5 or less staff. As a result many of these labs relied on consultants and contractors with specialised skills to function effectively.
 In Australia all of the agency-owned & led innovation units were focused on a single (funding) agency, whereas New Zealand has established two cross-government units, which work broadly across government.
In Australia all of the agency-owned & led innovation units were focused on a single (funding) agency, whereas New Zealand has established two cross-government units, which work broadly across government.
Interestingly most staff at government-based units were long-term public servants. These units did not draw significantly on external talent from Australia's innovation networks - which raises alarm bells for me in terms of building a blend of talent with broad experience across the innovation ecosystem.
My personal experience with these innovation units has been mixed. Some are still very locked into public sector norms, and find it difficult to produce more than iterative innovations, whereas others have embraced the freedom to innovate and are already providing significant returns. In my experience the more diverse the staff experience, and the more 'liberated' from public sector norms, the more effective these units tend to be.
The areas of policy these units worked in were quite diverse, ranging across 'social issues, housing and welfare’, ‘Public administration and governance’, ‘Education’, ‘Health’, ‘Indigenous and Maori issues’, ‘Transport’ and ‘Policing, crime, and the justice system’ - a good sign that the value and need for innovation is being recognised broadly across government, if not deeply.
Now while I have had concerns about some of these units turning into 'innovation ghettos' - where agencies tend to look to these units to provide the bulk of innovation within agencies, there are strong signs - particularly in New Zealand - that in many cases these units are functioning more as facilitators and amplifiers for innovation rather than innovation mines.
In my view there's plenty of innovation across government and the long-term challenges to realising this innovation as progressive improvement of government services, effectiveness and efficiency have included hierarchies stifling innovation based on source, poor pitch/amplification skills, limited capability to scale & execute, perceptual fears and budget mismatches.
If government innovation units can address these challenges effectively, then the future for these units looks bright.
However underneath the politics, government agencies across Australia and New Zealand have been vigorously expanding their innovation capability, as the The Policy Lab at Melbourne University recently reported.
"A vibrant public sector innovation landscape is emerging in Australia and New Zealand. Public sector innovation (PSI) units are increasingly being established by governments to bring new insights and approaches to policy design and the delivery of public services."The Mapping Public Sector Innovation Units in Australia and New Zealand 2018 Survey Report identified at least 26 PSI units across Australian and New Zealand government at different levels, across agency-run, agency-led and industry-led units - and that only counts the units the researchers were able to identify, which missed units such as The Garden from Accenture and some deeply embedded innovation teams within certain government organisations.
Notably a number of these units remain new, with a quarter less than 12 months old, and more than half less than two years old, and small, with half employing 5 or less staff. As a result many of these labs relied on consultants and contractors with specialised skills to function effectively.
 In Australia all of the agency-owned & led innovation units were focused on a single (funding) agency, whereas New Zealand has established two cross-government units, which work broadly across government.
In Australia all of the agency-owned & led innovation units were focused on a single (funding) agency, whereas New Zealand has established two cross-government units, which work broadly across government.Interestingly most staff at government-based units were long-term public servants. These units did not draw significantly on external talent from Australia's innovation networks - which raises alarm bells for me in terms of building a blend of talent with broad experience across the innovation ecosystem.
My personal experience with these innovation units has been mixed. Some are still very locked into public sector norms, and find it difficult to produce more than iterative innovations, whereas others have embraced the freedom to innovate and are already providing significant returns. In my experience the more diverse the staff experience, and the more 'liberated' from public sector norms, the more effective these units tend to be.
The areas of policy these units worked in were quite diverse, ranging across 'social issues, housing and welfare’, ‘Public administration and governance’, ‘Education’, ‘Health’, ‘Indigenous and Maori issues’, ‘Transport’ and ‘Policing, crime, and the justice system’ - a good sign that the value and need for innovation is being recognised broadly across government, if not deeply.
Now while I have had concerns about some of these units turning into 'innovation ghettos' - where agencies tend to look to these units to provide the bulk of innovation within agencies, there are strong signs - particularly in New Zealand - that in many cases these units are functioning more as facilitators and amplifiers for innovation rather than innovation mines.
In my view there's plenty of innovation across government and the long-term challenges to realising this innovation as progressive improvement of government services, effectiveness and efficiency have included hierarchies stifling innovation based on source, poor pitch/amplification skills, limited capability to scale & execute, perceptual fears and budget mismatches.
If government innovation units can address these challenges effectively, then the future for these units looks bright.
Tags:
collaboration,
digitalgov,
gov2au,
innovation
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)




